Anatomy of Root
Anatomy of Root: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Anatomy of Dicot Root, Anatomy of Monocot Root, Anatomy of Root, Vascular Bundle of Dicot Root and, Vascular Bundle of Monocot Root
Important Questions on Anatomy of Root
In monocot stem, hypodermis is:
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called
Four radial vascular bundles are found in
In monocot roots which types of vascular bundles are found?
Well-developed pith is found in
The layer of cells between endodermis and vascular bundles is called
In roots, lateral branches arise from
Which of the following is seen in monocot root?
If four radial vascular bundles are present, then the structure will be
In the diagram of T.S. of the stele of dicot root, the different parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets correctly match with the parts they indicate:
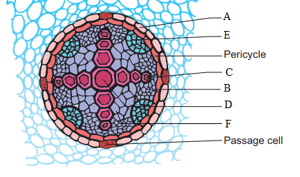
Which of the following is seen in a monocot root?
Consider the following statements
(A) In a dicot root, the vascular bundles are collateral and endarch
(B) The inner most layer of cortex in a dicot root is endodermis
(C) In a dicot root, the phloem masses are separated from the xylem by parenchymatous cells that are known as the conjunctive tissue
Of these statements given above
The layer of cells outside the phloem meant for giving rise to the root branches is called
Casparian strips are present in the ____of the root
How many histogens are present at the apex of root
Epiblema in roots is derived from
Histogen theory is more applicable for
The calyptrogen of the root apex forms
Which one of the following options correctly represents the tissue arrangement in roots
A transverse section of a typical monocot root shows,
(a) Barrel-shaped endodermal cells with Casparian strips.
(b) Diarch to hexarch vascular bundles.
(c) Protoxylem towards centre and metaxylem towards the periphery.
(d) Large well-developed parenchymatous pith in centre.
